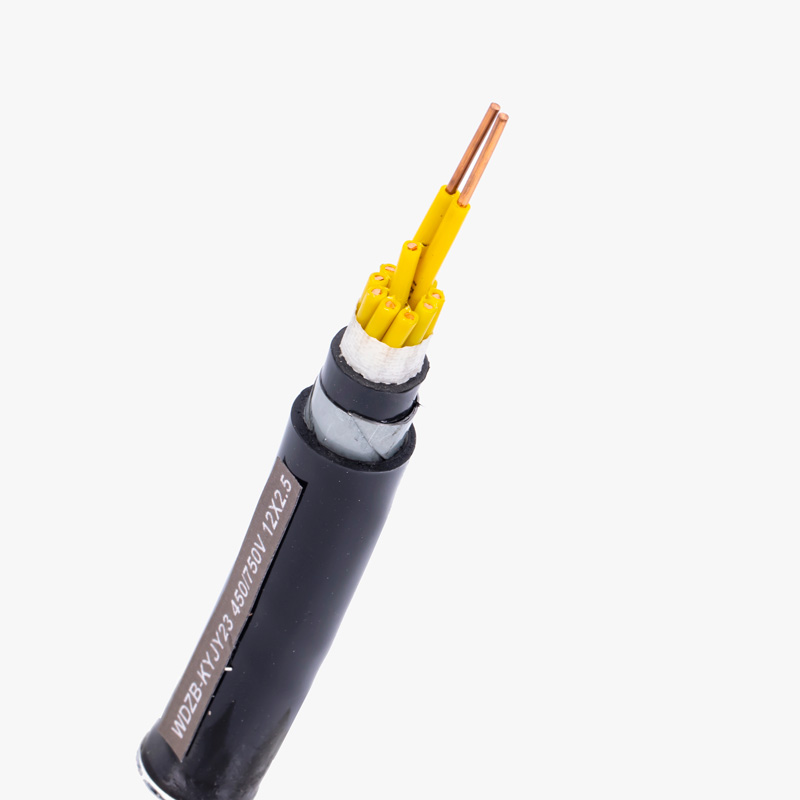
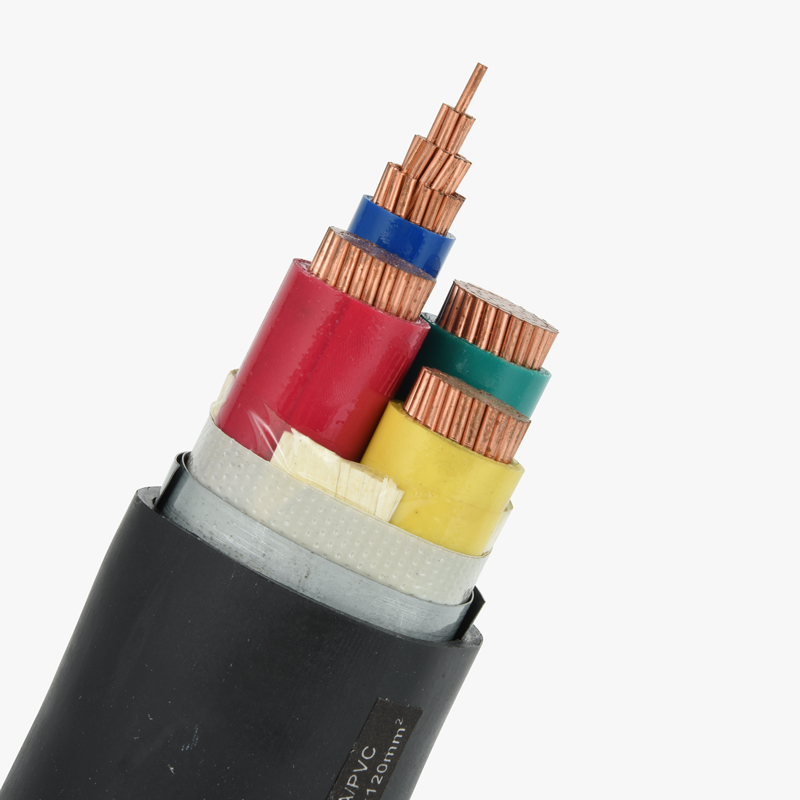
What is PVC insulation?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) insulation is a widely used material in the manufacturing of cables, offering both electrical and physical protection. This thermoplastic polymer is often used to cover electrical conductors, providing insulation that resists heat, moisture, and chemical corrosion. PVC-insulated cables are durable, cost-effective, and adaptable, making them an ideal choice for various industrial, commercial, and residential applications.

Benefits of PVC Insulation
PVC insulation offers a range of benefits, including high resistance to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. It is flexible, cost-effective, and has excellent electrical properties. Moreover, PVC cables can withstand a variety of environmental conditions, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications. Manufacturers appreciate its ease of processing and durability, ensuring a long service life for cables and wires.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Resistance to Moisture | PVC insulation is highly resistant to moisture, ensuring that cables remain protected in damp or humid environments, reducing the risk of electrical faults. |
| Chemical Resistance | PVC provides excellent resistance against various chemicals, making it suitable for use in industrial environments where cables may be exposed to corrosive substances. |
| Abrasion Resistance | PVC insulation is durable and resistant to abrasion, helping prevent damage from physical wear and tear in high-stress applications. |
| Flexibility | Despite its durability, PVC is flexible, allowing easy installation in tight spaces and around corners without cracking or breaking. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | PVC is a relatively low-cost material, making it an affordable choice for a wide range of applications, offering great value for the protection it provides. |
| Electrical Properties | PVC offers excellent electrical insulating properties, preventing the flow of electrical current through the insulation and reducing the risk of electrical shock. |
| Environmental Adaptability | PVC can withstand a variety of environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures and exposure to UV light, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations. |
| Durability | PVC insulation enhances the longevity of cables by offering protection against environmental factors, ensuring long-term reliability and performance. |
| Ease of Processing | PVC is easy to process and manufacture, allowing manufacturers to produce high-quality cables quickly and efficiently, ensuring consistent product quality. |
Application fields of PVC insulated cables
PVC-insulated cables are commonly used in power distribution, telecommunications, and industrial control systems. They are ideal for applications where flexibility and durability are important. Companies like Qrunning Cable offer a variety of PVC cables that are used in environments ranging from residential wiring to complex industrial machinery setups.
Keep reading to explore more about the benefits, applications, and technical aspects of PVC insulation.
Is PVC a good heat insulator?
PVC is not an excellent heat insulator compared to other materials like rubber or ceramic. However, it offers moderate heat resistance, which makes it suitable for most standard applications. PVC insulation can typically withstand temperatures ranging from -15°C to 70°C, though it can degrade at higher temperatures. For electrical applications, PVC cables are often used where exposure to extreme heat is not a primary concern. Manufacturers tend to choose PVC for environments where moderate heat resistance is sufficient, but for higher-temperature applications, other materials like silicone or Teflon are often preferred. In addition, PVC’s insulating properties make it a suitable material for everyday electrical and cable applications in non-extreme conditions.
Is PVC a good electrical insulator?
Yes, PVC is an excellent electrical insulator. Its insulating properties are one of the main reasons for its widespread use in cable manufacturing. PVC prevents the flow of electricity through the outer layer of cables, making it an effective barrier that protects users from electrical shocks. It also helps reduce the risk of short circuits by ensuring that electrical conductors are safely enclosed. PVC insulation’s dielectric strength allows it to withstand electrical voltage without breaking down, which is why it’s a go-to material for cables used in power distribution and telecommunications. When compared to other insulating materials, PVC is both cost-effective and efficient, offering solid electrical performance across a wide range of applications.
What Are the Drawbacks of PVC Insulation?
Despite its many advantages, PVC insulation does come with a few drawbacks. One of the main issues is its limited heat tolerance. As mentioned earlier, PVC begins to degrade at higher temperatures, which means it’s unsuitable for extremely high-temperature environments. Additionally, PVC is not as environmentally friendly as other materials, as its production and disposal can release harmful toxins into the environment. Another concern is its flammability—while PVC is fire-retardant, it can still catch fire under certain conditions, and the burning of PVC releases toxic fumes. Lastly, PVC can become brittle over time when exposed to UV radiation, which limits its use in outdoor applications unless specially treated for UV resistance. These drawbacks make it important to assess the suitability of PVC insulation for specific applications.
Where Is PVC Insulation Used?

PVC insulation is used in a variety of applications, from residential to industrial
settings. Common uses include power cables, wiring for home appliances, and data transmission cables. It’s also widely used in automotive, telecommunications, and HVAC systems. In industrial settings, manufacturers often choose PVC-insulated cables for equipment and machinery that require durability and flexibility in installation. Additionally, PVC is a popular choice for low-voltage and medium-voltage cables due to its excellent electrical insulating properties and cost-effectiveness. For specific applications like industrial machinery, automotive wiring, or residential electrical systems, suppliers provide PVC cables tailored to meet industry standards and regulations.