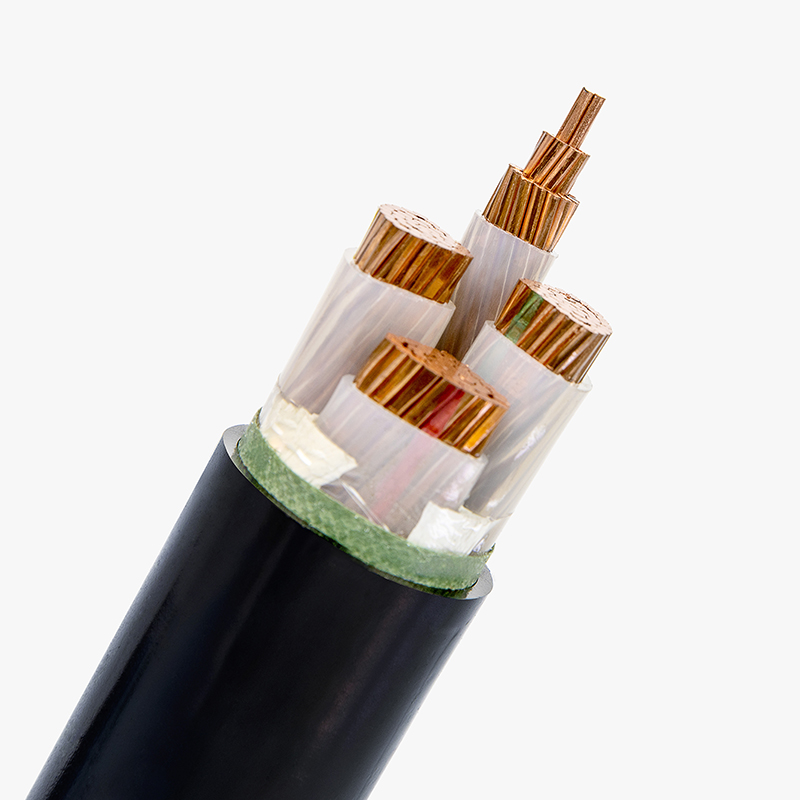
Are you struggling to find reliable high voltage cable manufacturers who deliver high-quality products on time? Poor-quality cables can lead to serious electrical failures and project delays. Trustworthy manufacturers like us provide the solution with durable, certified cables that meet high voltage specifications.
High voltage cables play a crucial role in powering industries, electric vehicles (EVs), and power grids. They come in various types such as high voltage DC and AC cables, each designed to meet specific needs for transmitting electrical power efficiently and safely.
Continue reading to explore the different types of high voltage cables and their functions, helping you make informed sourcing decisions.
Which Type of Wiring Is Used for High Voltage?
High voltage wiring involves cables specifically designed to handle elevated electrical load safely. These cables are made of materials that insulate and protect against electrical discharge. The primary types of wiring used for high voltage applications are:
- High Voltage AC Cables (HVAC): Used for transmitting alternating current (AC) power over long distances.
- High Voltage DC Cables (HVDC): Designed for direct current applications, these are often used in long-distance power transmission due to their efficiency.
- High Voltage Underground Cables: Used in urban settings to prevent exposure to weather conditions and physical damage.
Which Cable Transmits Electrical Energy at the Highest Voltage?
High voltage direct current (HVDC) cables are typically the most effective for transmitting electrical energy at extremely high voltages. HVDC systems are often used for long-distance, high-capacity transmission of electrical power, as they experience lower losses compared to AC cables. These cables are designed to carry voltage levels up to 500kV and above, making them suitable for power plants and large-scale energy distribution.
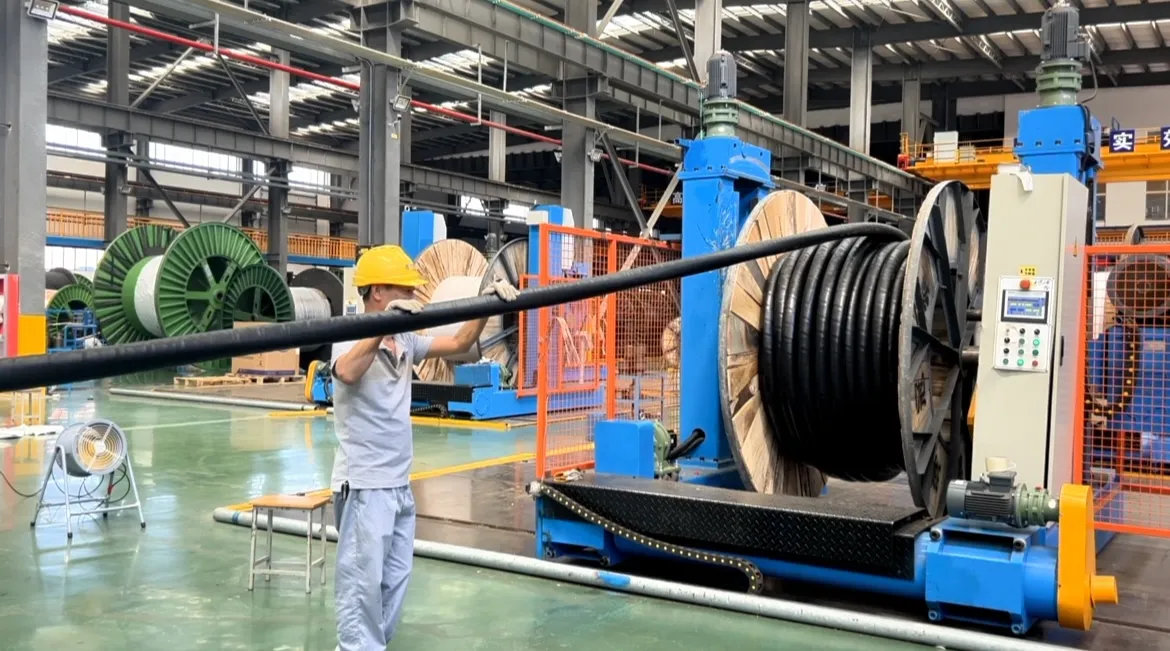

What Cable Is Used for High Voltage?
High voltage cables used for industrial and power grid applications include both AC and DC types. They must adhere to strict specifications for insulation and material quality to handle the immense power load. Key types include:
- High Voltage AC Cable: Typically used in power transmission lines, it is insulated with materials that prevent energy leakage.
- High Voltage DC Cable: Utilized in renewable energy plants and intercontinental electrical grids, it ensures high-efficiency power delivery over long distances.
- High Voltage Underground Cable: Designed to provide safety and reliability in urban environments.

What Is the Function of High Voltage Cable?
High voltage cables are designed to transmit electrical energy at higher voltages. They ensure the safe and efficient delivery of power from energy sources, such as power plants, to end-users or grids. These cables provide insulation to prevent energy leakage, ensuring safety in environments with high energy loads. Additionally, they are constructed to withstand extreme weather conditions, physical damage, and chemical exposure.
What Is the Difference Between HVDC and HVAC?
The primary difference between HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) and HVAC (High Voltage Alternating Current) lies in how they transmit power. HVDC cables are used for long-distance, efficient power transmission with lower energy losses, whereas HVAC cables are ideal for power grids and areas where alternating current is required. The conversion of AC to DC also reduces costs over long-distance transmission, making HVDC more effective for large-scale infrastructure projects.
Summary
Choose reliable high voltage cable manufacturers to ensure safe, efficient power transmission and high-quality cables for your projects. Qrunning Your reliable partner.
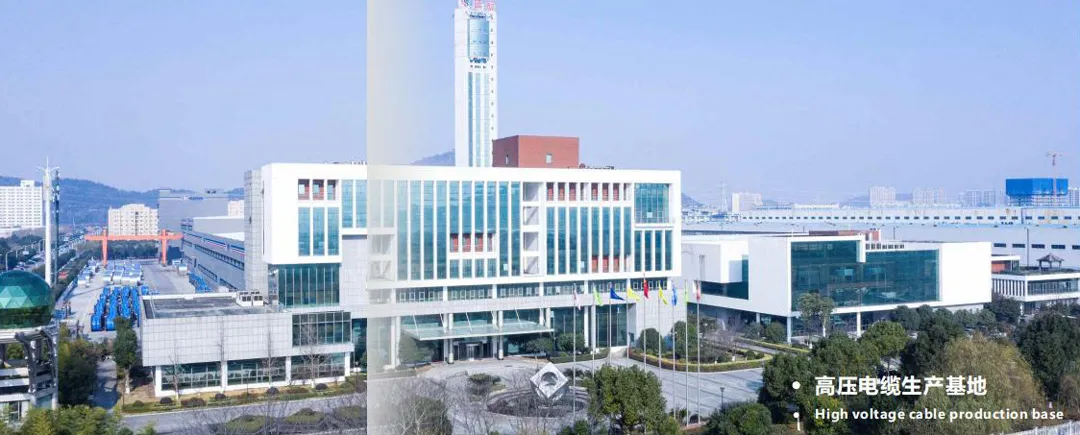
About Qrunning
Qrunning is a professional engaged in wire and cable research & development, production, sales and service enterprises.The main products are three series of wires and cables of 500kV and below.Qrunning started in 1990 and entered the top 50 of China’s cable industry in 2015.Dedicated high-voltage cable production base established in 2011.