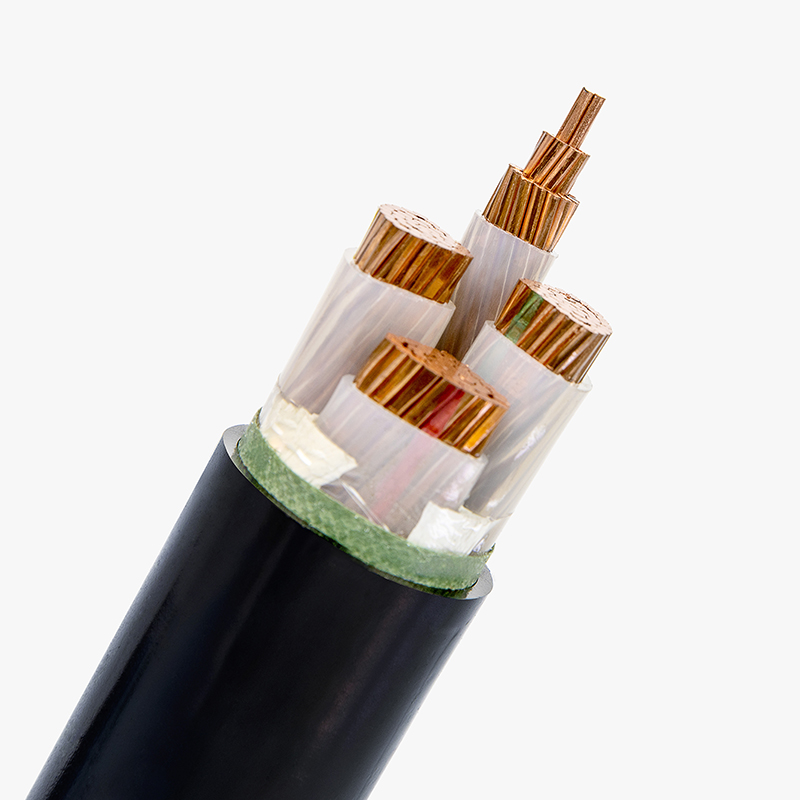
Low Voltage Cables Specifications
Low voltage cables are designed for energy-efficient applications where the operating voltage is under 1,000V, suitable for both residential and commercial projects. Quality certifications and accurate specifications are crucial for performance and safety.
Low-Voltage Cable Types
Understanding the variety of low-voltage cables is essential for choosing the right one for your application. Below are detailed insights into the different types of low-voltage cables.
What are low voltage cables?
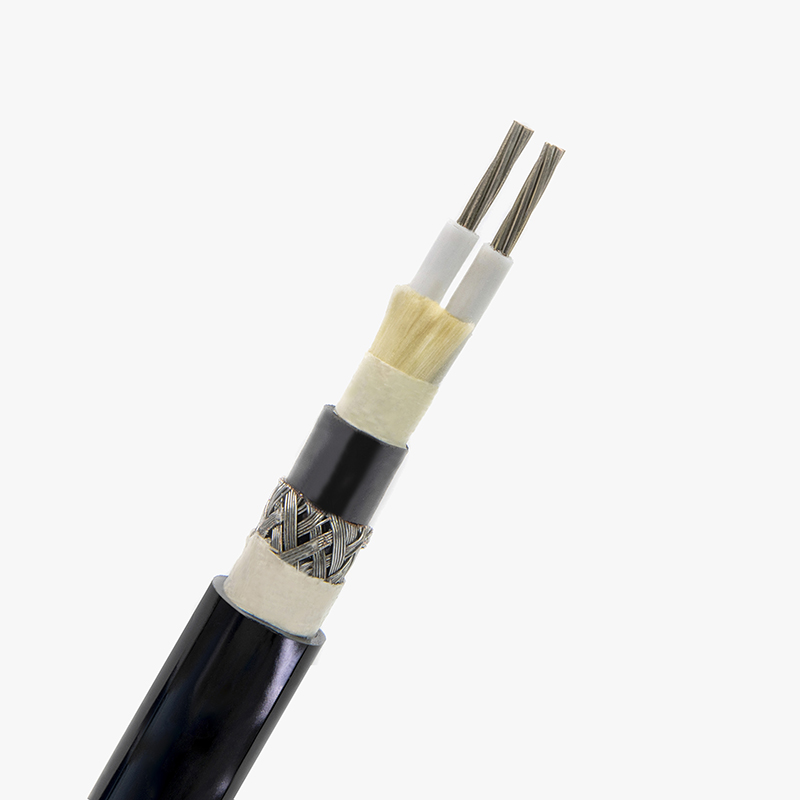
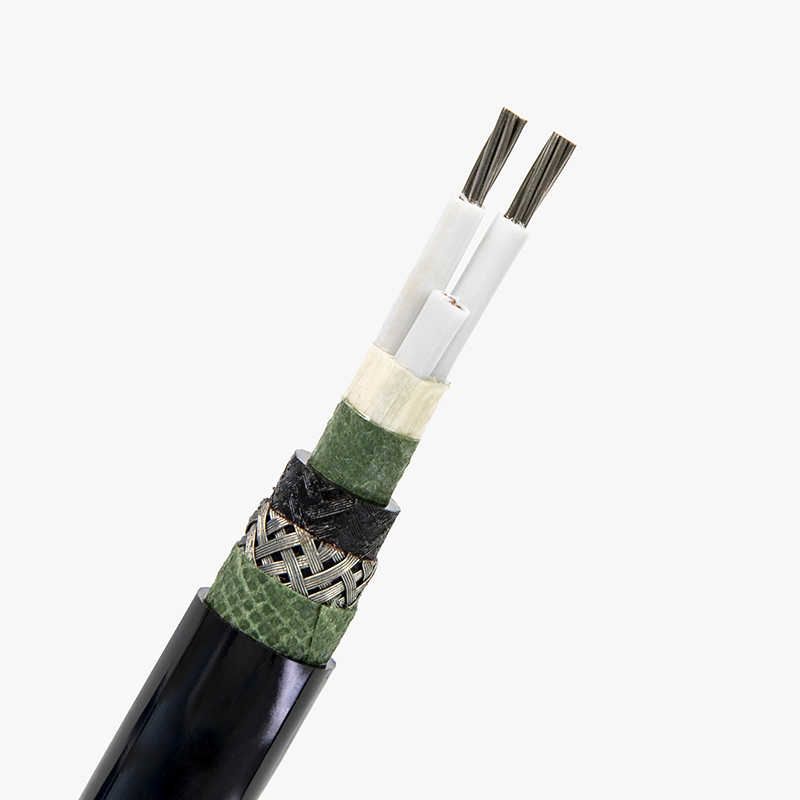
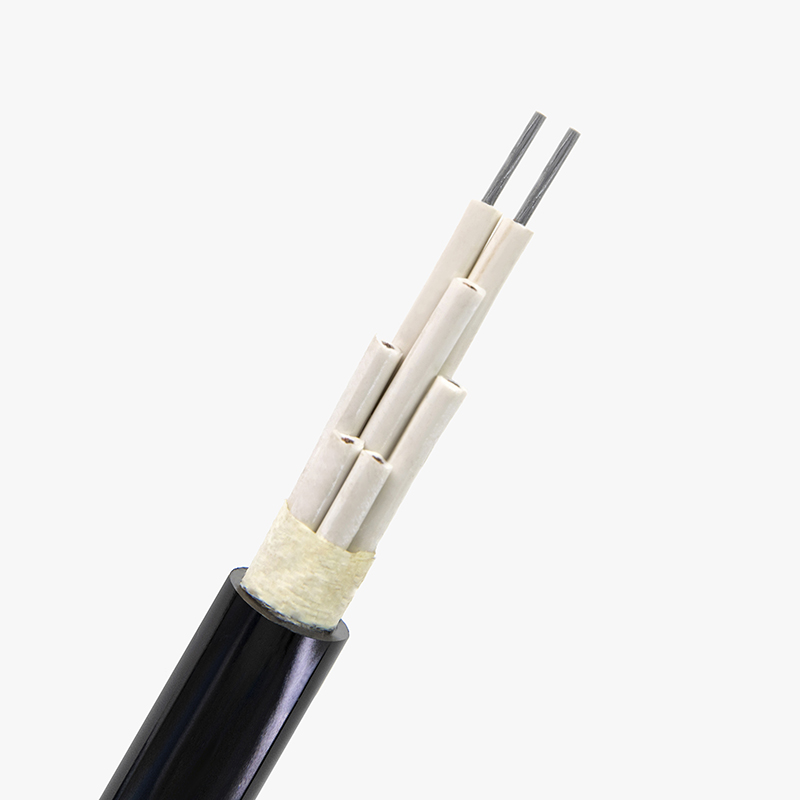
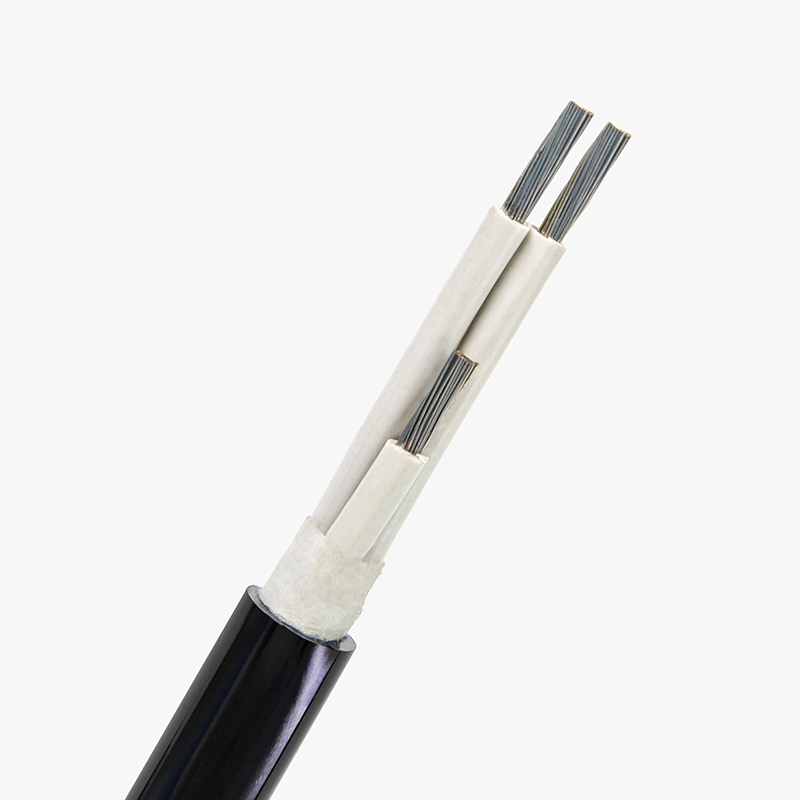
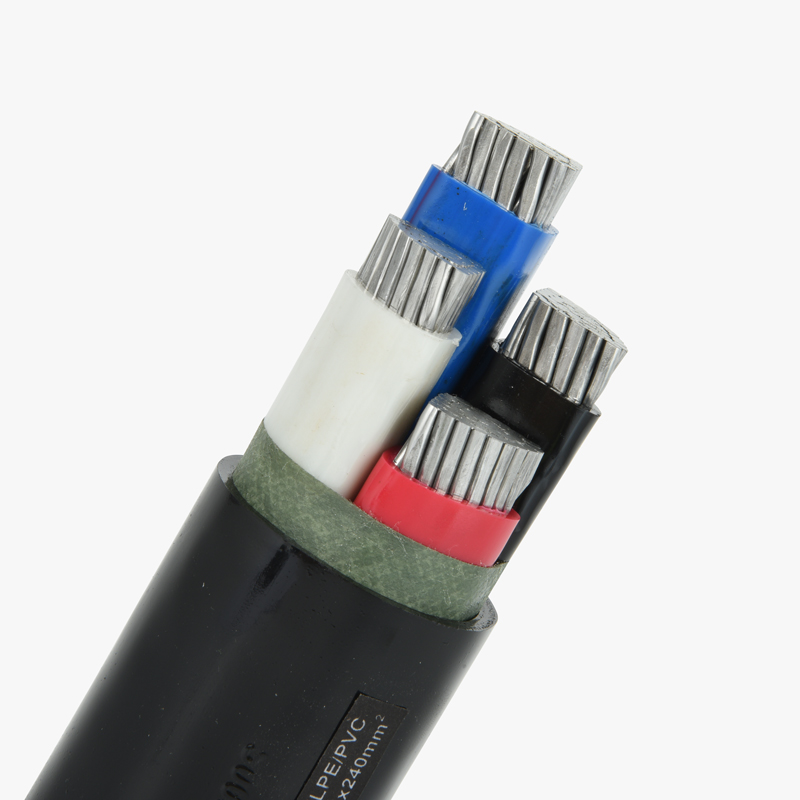
Low voltage cables are used to carry electrical energy at voltages typically less than 1,000 volts. These cables are essential for numerous applications, from powering appliances in homes to connecting equipment in commercial buildings. They come in various types, such as single-core, multi-core, armored, and non-armored, providing flexible solutions for different environments. The low voltage designation is crucial for safety, as it indicates the cable’s ability to handle electricity safely without the risk of overheating or fire under normal conditions.
What’s standard conductor material for low-voltage cable?
The standard conductor materials for low-voltage cables are copper and aluminum. Copper is the most commonly used material due to its excellent conductivity, which ensures minimal energy loss over long distances. Aluminum, while less conductive than copper, is often chosen for its cost-effectiveness and lighter weight, making it a popular choice for long-distance cable runs. The choice of conductor material can influence the overall cost, performance, and longevity of the cable, which is why it’s important to understand the differences and choose based on the specific needs of the project.
What are the best low voltage cabling companies?
Some of the best low-voltage cabling companies are those that have a proven track record of producing high-quality, certified cables that meet international safety standards. Leading manufacturers like QRUNNING are known for their extensive experience, top-tier production capabilities, and strong commitment to customer satisfaction. When choosing a supplier, it’s important to consider factors such as product quality, pricing, delivery capabilities, and customer service. Companies with certifications like ISO and UL standards are often the most reliable for high-performance cabling solutions.
What’s the difference between low voltage cable and wire?
The main difference between low voltage cables and wires lies in their construction and intended use. A cable typically consists of multiple wires that are bundled together and insulated for safety. It can have several conductors (wires), each carrying electrical current, and is typically used for larger installations. On the other hand, a wire is usually a single conductor, and while it may be used for low-voltage applications, it is less flexible for more complex setups. Cables provide enhanced protection from external factors, while wires are more suitable for simpler, localized applications.
How far can you run low voltage cable?
The distance over which you can run low-voltage cable depends on several factors, including the type of cable, the current being carried, and the level of voltage drop you’re willing to tolerate. In general, for a typical low-voltage application (under 1,000V), it’s advisable to keep the cable run under 100 meters to ensure minimal voltage loss and safe operation. Longer runs may require thicker cables to reduce energy loss. Factors like cable insulation and external interference can also affect the maximum distance, so it’s important to consider these variables when planning your installation.
Conclusion
Low-voltage cables are essential for energy-efficient electrical systems. Choosing the right type, conductor material, and supplier ensures safety and optimal performance for your project.